Generating random numbers in Excel might seem straightforward, but truly mastering the art—especially when you need unique, non-repeating values—can revolutionize your data analysis, simulations, and decision-making processes. From basic randomization to sophisticated methods for ensuring uniqueness, Excel offers a powerful suite of tools that can meet a wide array of needs. This super pillar hub is your definitive guide to becoming an Excel random number maestro, ensuring your outputs are not just random, but precisely what you need.
The Foundations: Understanding Core Random Number Functions in Excel
At the heart of Excel's random number capabilities are three fundamental functions: RAND(), RANDBETWEEN(), and RANDARRAY(). Each serves a distinct purpose, laying the groundwork for more complex random number generation.
- RAND(): This function is your entry point, generating a random decimal number between 0 (inclusive) and 1 (exclusive). It's incredibly versatile for scaling to any range, for instance,
RAND() * (b - a) + afor decimals between 'a' and 'b', or wrapped inINT()for integers. - RANDBETWEEN(bottom, top): For those times you need a quick random integer within a specific range,
RANDBETWEEN()is your best friend. Simply specify the bottom and top values, and Excel delivers an integer, inclusive of both ends. It simplifies the process considerably compared to theINT(RAND() * ...)approach. - RANDARRAY(rows, columns, min, max, whole_number): Available in Excel 365 and Excel 2021,
RANDARRAY()is a dynamic array powerhouse. It can generate an array (or range) of random numbers with specified dimensions, minimum/maximum values, and the option to return whole numbers or decimals. This function drastically streamlines tasks that previously required multiple steps or an array formula.
While these functions are excellent starting points, they often recalculate every time your worksheet changes, potentially leading to new random numbers whenever you open or modify your file. To dive deeper into the basics and get comfortable with these foundational tools, you should Learn about RAND and RANDBETWEEN and discover how to harness their full potential.
Unlocking Uniqueness: Generating Random Numbers Without Repeats
The real challenge often arises when you need unique random numbers – values that do not repeat within a given set. Whether you're drawing raffle winners, assigning unique IDs, or creating non-repeating samples, Excel provides several robust methods to achieve this, spanning both modern dynamic array functions and traditional approaches.
Dynamic Array Functions for Unique Outputs (Excel 365, 2021)
Modern Excel versions (365, 2021) offer elegant solutions for unique random number generation using dynamic array functions. These methods are typically more efficient and require less setup.
- UNIQUE & RANDARRAY: This powerful combination directly generates a list of unique random numbers. For example,
=UNIQUE(RANDARRAY(10, 1, 1, 100, TRUE))will produce 10 distinct random integers between 1 and 100. TheUNIQUEfunction filters out any potential repeats fromRANDARRAY's output, ensuring your list is truly unique. - SORTBY & SEQUENCE: This method is fantastic for shuffling a predefined sequence of numbers.
SEQUENCE(N)creates an ordered list (e.g., 1 to 10), andRANDARRAY(N)generates a corresponding list of random numbers.SORTBYthen uses these random numbers to reorder theSEQUENCE, effectively creating a unique, random permutation. An example is=SORTBY(SEQUENCE(10), RANDARRAY(10)). - INDEX with UNIQUE, RANDARRAY, & SEQUENCE: This approach offers incredible flexibility for generating unique random numbers of various types and within specific ranges or dimensions. By drawing from a larger pool of unique
RANDARRAYvalues usingINDEXandSEQUENCE, you can construct arrays of unique integers or decimals tailored to your exact needs.
Traditional Approaches for Unique Randomness (All Excel Versions)
For users on older Excel versions or those who prefer formula-based solutions without dynamic arrays, these methods remain highly effective.
- RAND & RANK Functions: This clever technique leverages the fact that
RAND()generates unique decimal numbers. By creating a column ofRAND()values and then using theRANK()function on these decimals, you'll produce a corresponding list of unique ranks, which serve as unique random numbers. For instance, if B5 contains aRAND()value,=RANK(B5,$B$5:$B$15)in a parallel column will give you a unique rank within that range. - RANK.EQ & COUNTIF Functions: When you need unique random numbers from a specific range (e.g., 10 to 50) and handle potential ties from
RANDBETWEEN, this combination provides a robust solution. It involves an adjustment formula that builds uponRANDBETWEENvalues to ensure uniqueness and set your desired starting point. - Analysis ToolPak Add-in: This built-in Excel add-in offers a non-formulaic way to generate various types of random numbers, including unique integers. Once enabled (File > Options > Add-ins > Excel Add-ins > Go > Analysis ToolPak), you can access "Random Number Generation" from the Data tab, specify your distribution (Uniform is key for uniqueness), range, and output.
For a deeper dive into these methods and to master the techniques for getting exactly the random numbers you need, you'll want to Unlock precise random number generation for all your unique and specific requirements.
Beyond the Basics: Practical Applications of Random Numbers
Generating random numbers isn't just a theoretical exercise; it has immense practical value across various professional and personal applications in Excel. From enhancing data privacy to making fair decisions, random numbers are surprisingly powerful.
- Simulations & Hypothesis Testing: Create diverse datasets for statistical simulations, modeling potential outcomes in business, science, or finance. Generate random samples to test hypotheses, ensuring your analysis is robust.
- Generate numbers with specific distributions: Beyond uniform random numbers, you can simulate data following normal, exponential, or other distributions using functions like
NORM.INV(RAND(), mean, standard_deviation). This is invaluable for realistic scenario modeling. - Anonymize and test data: Replace sensitive information (like customer IDs or account numbers) with random, non-identifiable values for privacy protection or when developing and testing systems without exposing real data.
- Make decisions: Use random selection for anything from drawing a winner in a contest to randomly assigning tasks. A simple
INDEX(range, RANDBETWEEN(1,COUNTA(range)))can pick a random item from a list.
These are just a few examples of how integrating random numbers can significantly boost your Excel capabilities. To explore the full spectrum of how random numbers can transform your workflow and analysis, Unlock Excel random number applications and see where they can take your projects.
Taking Control: Freezing and Advanced Techniques
One common characteristic of Excel's random number functions is their volatility; they recalculate every time the workbook changes. While often useful, this behavior can be problematic if you need to lock in a specific set of random values. Furthermore, for highly customized or automated random number generation, you might look beyond standard formulas.
Preventing Recalculation of Random Numbers
To "freeze" your random numbers and prevent them from changing:
- Copy and Paste Special as Values: Select the cells containing your random number formulas. Copy them (Ctrl + C). Then, right-click on the same selection (or a new destination) and choose "Paste Special > Values". This replaces the formulas with their current numerical results.
- F9 Key in the Formula Bar: For individual cells, click into the formula bar for the cell containing a random number formula, then press F9. This directly evaluates the formula and replaces it with its current value.
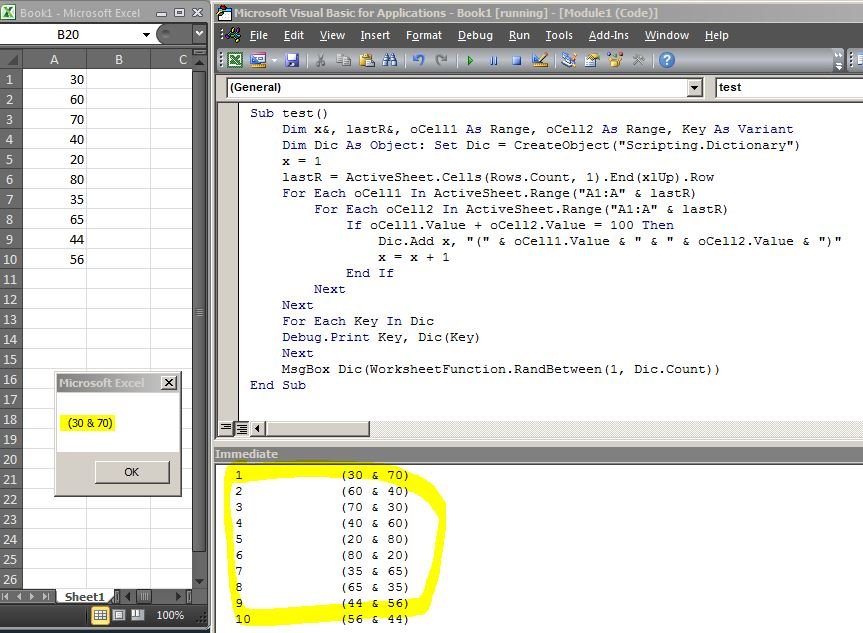
Advanced Random Number Generation with VBA
When standard Excel functions don't offer the precise control or automation you need, Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) steps in. VBA allows you to write custom macros to generate random numbers under very specific conditions, populate ranges, or even create unique random sequences based on complex logic that might be cumbersome with worksheet formulas alone. This is particularly useful for large-scale simulations or integrating random number generation into custom Excel applications.
Understanding how to control the recalculation of your random numbers is crucial for consistent data. For a comprehensive guide on managing this behavior, you should explore Freezing and Controlling Random Number. And if your needs extend to automation and highly customized scenarios, then Berikut beberapa pilihan: Master advanced VBA offers the tools to build sophisticated solutions.
Troubleshooting Common Issues with Dynamic Array Functions
While incredibly powerful, dynamic array random number functions (like RANDARRAY, UNIQUE, SEQUENCE) can occasionally throw errors. Knowing how to diagnose them will save you time.
- #CALC!: This error typically means the
UNIQUEfunction couldn't extract unique values, perhaps because the source array was too small or conditions made uniqueness impossible. - #SPILL!: This occurs when a dynamic array function tries to return multiple results, but there are existing values in the cells where it intends to "spill" its output. Clear the cells in the intended spill range to resolve.
- #VALUE!: In
RANDARRAY, this error usually indicates that theminargument is greater than themaxargument, a logical impossibility for number generation.
The Algorithm Behind the Magic
It's worth noting that since Excel 2010, the program utilizes the Mersenne Twister algorithm for its random number generation. This algorithm is widely recognized for generating high-quality pseudo-random numbers suitable for most statistical and simulation purposes.
Final Thoughts: Empowering Your Excel Workflow
Mastering random number generation in Excel, especially the techniques for producing unique outputs, equips you with a versatile toolkit for everything from scientific simulations to everyday decision-making. By leveraging both Excel's built-in functions and understanding their nuances, you can unlock new levels of efficiency and analytical power in your spreadsheets. Keep experimenting with these methods, and you'll find countless ways to enhance your data projects.